DENTAL CARIES
Dental caries is an infectious microbiology disease of the teeth that result is localized dissolution and destruction of the calcified tissue. It is the second most common cause of tooth loss and found universally , irrespective of age,sex,caste,creed,or geographic locations. It is considered to be a disease of civilized society, related to life style factor, but heredity also plays an important role.
In the late stage,it cause pain ,is expensive to treat and leads to loss of precious man-hour. However, it is presentable to a certain extent, The prevalence of dental caries in India is 50% - 60%.
ETIOLOGY:-
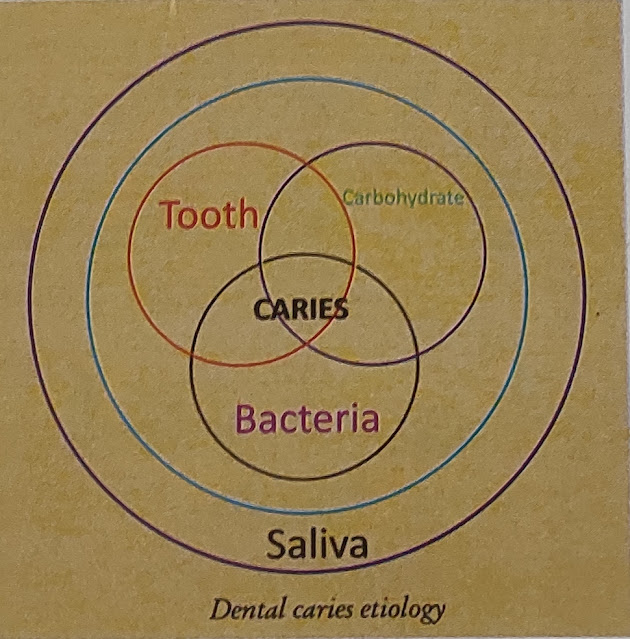
Interplay of three principal factor is responsible for this multi - factorial disease.
HOST :- Teeth and saliva.
AGENT :- Microorganisms in the form of dental plaque (caries)which is discussed below.
SUBSTRATE:- Diet.
Thus , caries requires are susceptible host , cariogenic oral flora and a suitable substrate, which must be present for a sufficient length of time.
1. TEETH:-
a). Composition:- Deficiency of certain trace elements in diet such as fluorine,zinc,lead and iron during tooth development result in enamel which is more susceptible to dental caries.
b). Morphological characteristics:- Deep, narrow occlusal fissures, and lingual and buccal pits. Tend to trap food debris and bacterial, which can cause caries. As teeth get worth during mastication ( altrition ) incidence of caries decline.
c). Position:- The inter dental area are more susceptible to dental caries, crowding of teeth or abnormal spacing between the teeth can increase the susceptible to carries.
2. SALIVA :- Saliva has a cleansing effect on the teeth, Normally, 700 - 800 ml of saliva is secreted per day, caries actually increases. Eating fibrous food and chewing vigorously increases salivation, which helps in digestion as well as improves the cleansing effect on the teeth. The quantity ( Reduced salivary secretion as found in xerostomia and salivary gland aplasia gives rise to increase caries activity ) as well as composition, PH , Viscosity of the saliva plays an important role in dental caries.
3. AGENT:- MICROORGANISMS:-
DENTAL PLAQUE:- It is a this, tenacious Microbial film dead form on the tooth surfaces microorganism is the dental plague ferment carbohydrates foodstuffs, especially the disaccharides like surose, to produce acid that cause demineralization of inorganic substance and furnish various proteolytic enzyme to cause distintegsation of the organic substance of the teeth , the processes involved in the initiation and progression of dental caries. The dental plaque holds the acids to produced in cross contact with the tooth surface and prevents them from cleansing action of Saliva.
FUNCTIONS OF DENTAL PLAQUE:-
Salivary protein form a thin film called pellicle on the tooth surface.
⬇️ In 2hrs
Bacterial colonization ,desquamated epithelial cells and food debris.
⬇️ In 2 hrs
Plaque microorganisms predominantly streptococci
⬇️ Mature plaque
Mixed flora of cocci, bacilli , spirochaetes and and filamentous organism .
SUBSTRATE : FORMENTABLE CARBOHYDRATES :-
The role of refined carbohydrate, especially the disaccharides Surose in the ETIOLOGY of dental carries is well established. The total amount consume as well as the physical form, it's oral clearance rate and frequency of consumption are important factor in the ETIOLOGY.
The disaccharides Surose and lectose is fermented by plaque bacteria and produce Acids which is demineralised the enamel. The pH of resting saliva is 6.2. After taking sugar solution, with in 10 minutes, the pH of saliva drops to 2, which then gradually returns to baseline level over 30 to 60 minutes depending on type of sweet food consume take food take longer than the other solid food to get cleared from mouth and liquid is cleared the fastest . Saliva helps to wash away the acids produce. Therefore, decrease salivation due to any reason, like sjogren's syndrome, medication or radiation etc, increase the carries incidence.
Plaque disruption by frequent brushing ( at least every 12 hour ) and rinsing the mouth provides protection against dental carries. vitamin A, D, K, B complex (B6) calcium, Phosphorus, fluorine , amino acid such as lysine and fat having inhabitory effect on dental careers.